
- HOW TO CALCULATE PARTICLE DISTRIBUTION IN IMAGEJ SOFTWARE WINDOWS 7
- HOW TO CALCULATE PARTICLE DISTRIBUTION IN IMAGEJ SOFTWARE DOWNLOAD
- HOW TO CALCULATE PARTICLE DISTRIBUTION IN IMAGEJ SOFTWARE WINDOWS
Images can be layed out in a grid-like fashion, aka a montage. In the Channels Tools window, switch to Color mode and select a channel of interest. The color representation in 8-bit and 16-bit images is defined by a color Lookup Table (LUT).įor single channel images, you can change the LUT by running these commands:įor multi-channel image, you can change the LUT by running these commands: The resulting image should contain a merge of the red and blue channels without the green channel component. Set the green channel to None and leave the other default settings.
Go to File > Open Samples > Fluorescent Cells. You can merge up to 7 different images into a single multi-channel image. The input images need to be of the same type (either 8-bit or 16-bit pixel encoding).
HOW TO CALCULATE PARTICLE DISTRIBUTION IN IMAGEJ SOFTWARE WINDOWS
Images displayed in separate windows can be merged into multi-channel composite images. This operation only works on multi-channel image stacks or RGB images. Individual image channels are displayed in separate windows. Go to File > Open Samples > Mitosis (26MB, 5D stack). Although the color information has been converted to gray, the pixel intensity values remain unchanged.Ħ Change back to Color, Click More >, select a new color. Uncheck selected channels and note how the channel overlay changes based on the selected images.ĥ Change to Grayscale. Move the channel slider and note how the display updates based on the selected channel.Ĥ Switch back to Composite mode.
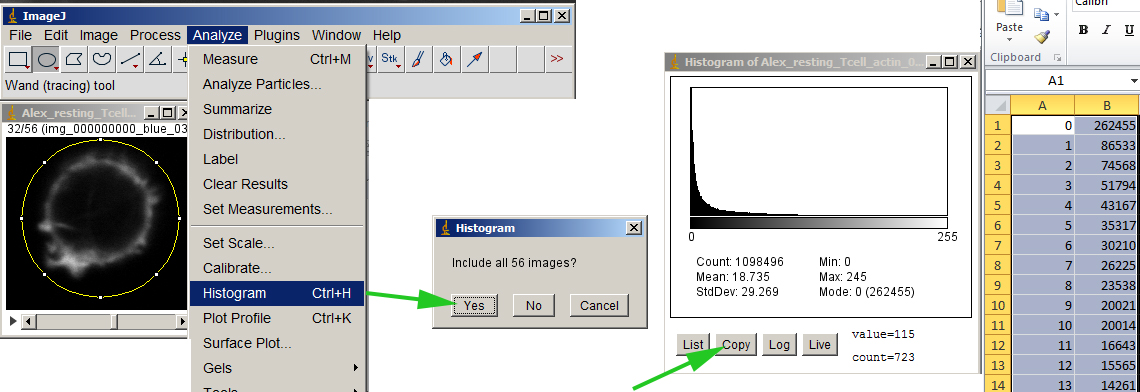
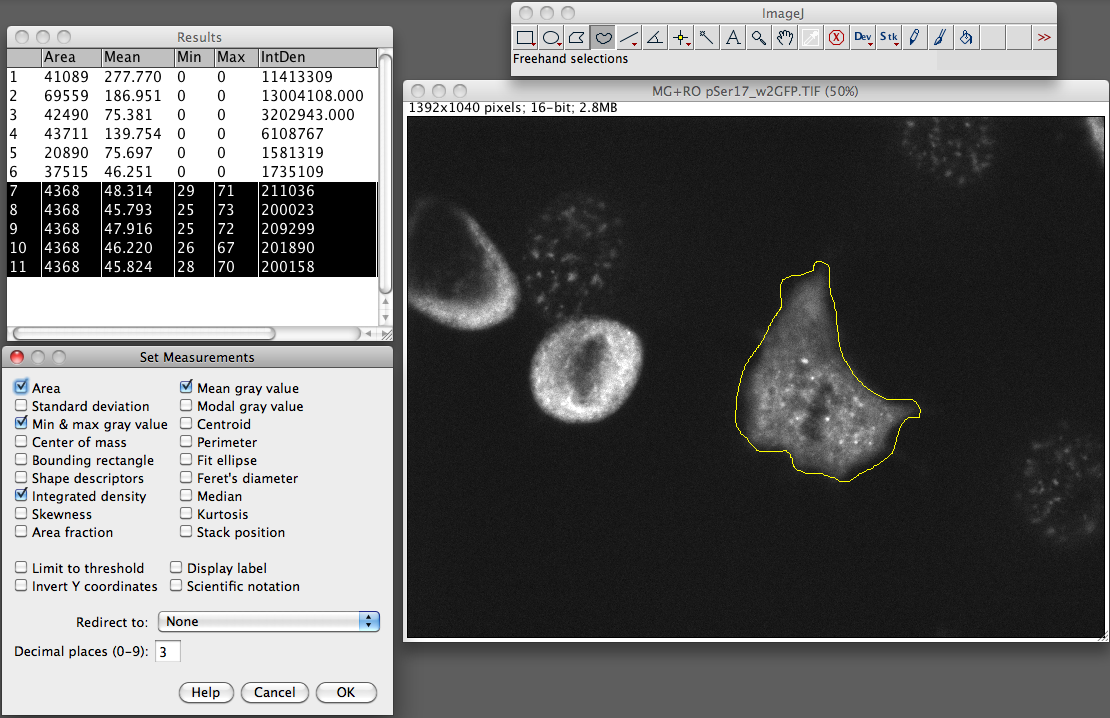
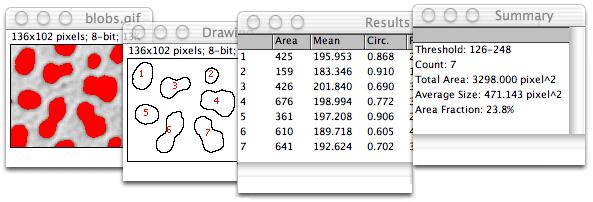
An image window should open as shown here.Ģ Open the Channels Tool dialog with Image > Color > Channels Tool….ģ In the Channels Tool dialog window, change from Composite to Color. For this example, open the 5-dimensional (x, y, z, color, time) image stack.ġ Go to File > Open Samples > Mitosis (26MB, 5D stack). Images and Image Stacks in Fiji Working with Image Channelsįiji has built-in tools to manipulate multi-channel composite and RGB images. Based on these masks, objects of interest can be classified and analyzed for size, geometry, pixel intensities, etc. The enhanced image can then be converted into binary image masks that define groups of pixels as objects. The cleaned-up image may then be processed to enhance certain features, e.g. The original image (or raw data) that serves as input for the image processing pipeline may contain background noise that may need to be removed by applying specifc image filters. Image processing and analysis procedures often share a common workflow as shown here. They are used for masking and segmentation of object areas of interest in an image. Pixels in grayscale images may be encoded as 8-bit integer (256 intensity levels), 16-bit integer (65536 intensity levels), or 32-bit float (decimal number) values.īinary images are a special type of 8-bit grayscale images that only contain the pixel values 0 (black) or 255 (white). RGB: 256 intensity values for red, green, and blue). color images (RGB, HSB, etc.), grayscale images, and binary images.Ĭolor images use 8-bit encoding for each channel (e.g. between 0-255)įiji can handle image files in various file formats and pixel encodings, e.g.
HOW TO CALCULATE PARTICLE DISTRIBUTION IN IMAGEJ SOFTWARE WINDOWS 7
Windows 7 & 10: The Fiji application should be installed in the user’s home directory rather than the default C:\Program Files directory.MacOS X: The Fiji application should be installed in the user’s home directory rather than the default Applications folder.
HOW TO CALCULATE PARTICLE DISTRIBUTION IN IMAGEJ SOFTWARE DOWNLOAD
To use Fiji, simply download and unzip the application, Fiji is available on Windows, Mac, and Linux platforms and can be downloaded directly


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
